|
The thyroid is a gland which is part of the endocrine system in the human body. It can be found
in the front of the neck just under the Adam’s apple. It has two lobes connected by a narrow neck, called an isthmus,
creating the shape of a butterfly. Each of the lobes is about 4cm long and 1-2cm wide. The thyroid gland is responsible for
the production of three hormones. Tetraiodothyronine, which is also known as thyroxine or T4 and triiodothyronine, also known
as T3 are peptides containing iodine. The thyroid gland also produces calcitonin. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which
is secreted by the pituitary gland, controls the production of these hormones. T3 and T4 play important roles within the body
and have many effects on metabolism, growth and development while calcitonin regulates calcium-phosphorus metabolism with
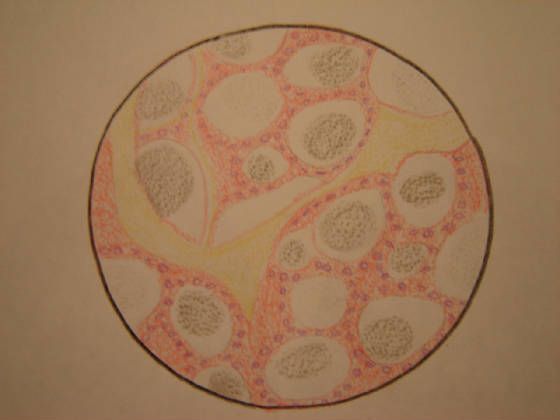
the body. The thyroid gland is comprised of follicles that absorb iodine from the bloodstream and concentrate it for the production
of the thyroid hormones. These follicles consist of a single layer of epithelial cells which secrete T3 and T4. Between the
follicles are spaces which are filled with parafollicular cells, which secrete calcitonin.
|